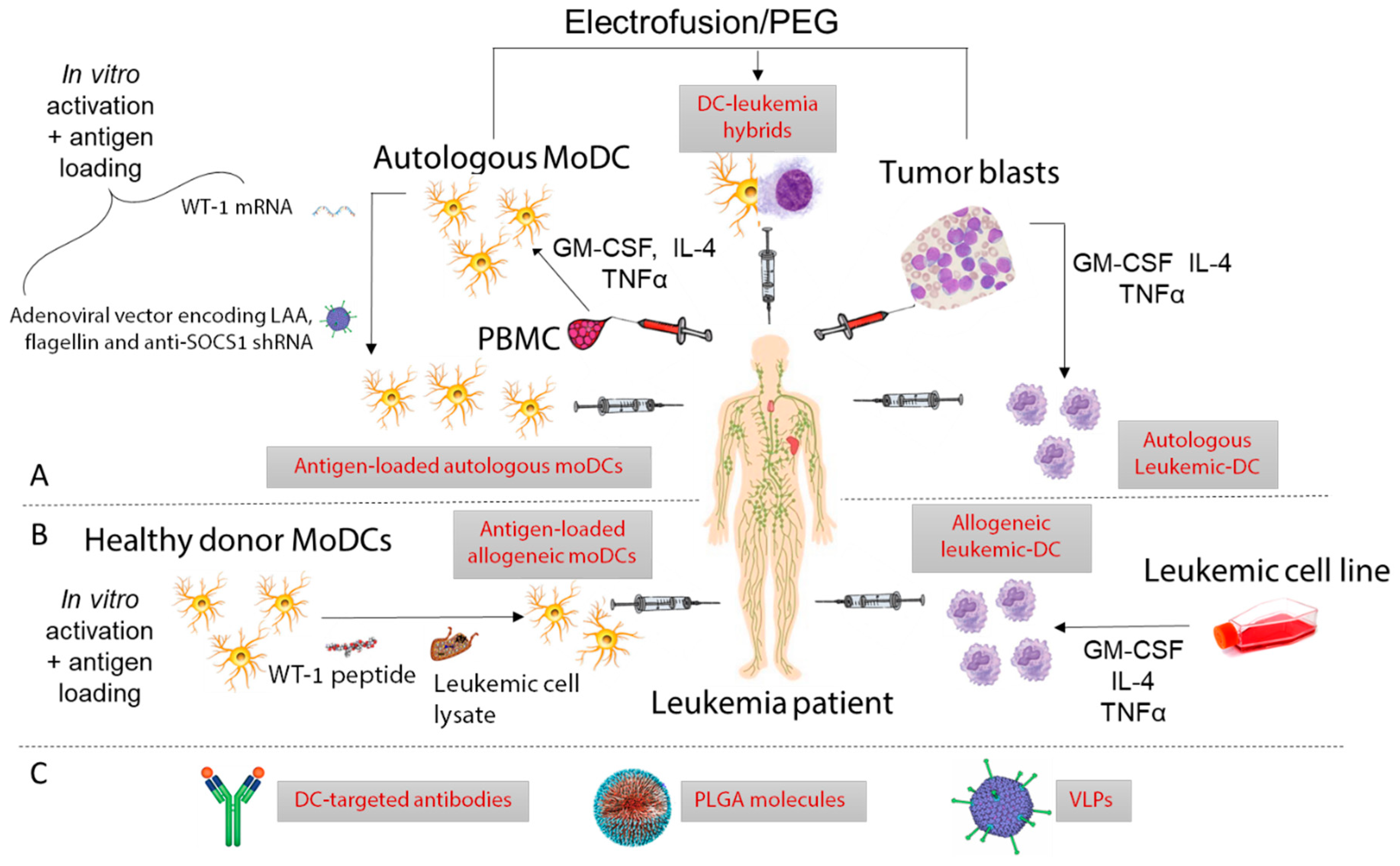
Dendritic cells dcs are essential in immunity owing to their role in activating t cells thereby promoting antitumor responses.
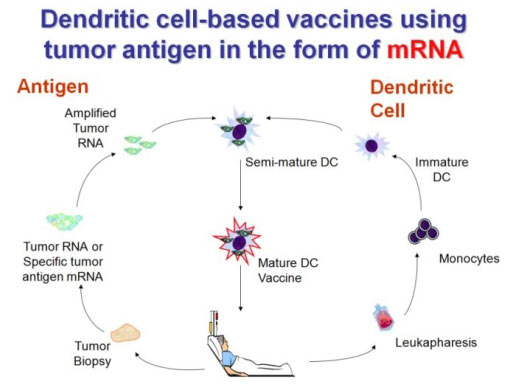
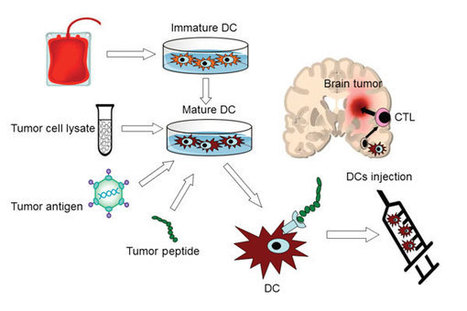
Overview of dendritic cell vaccines for brain tumors.
It s made with tissue from each participant s brain tumor.
4 clinical trials underway have demonstrated the successful application of dc vaccines to induce antitumor.
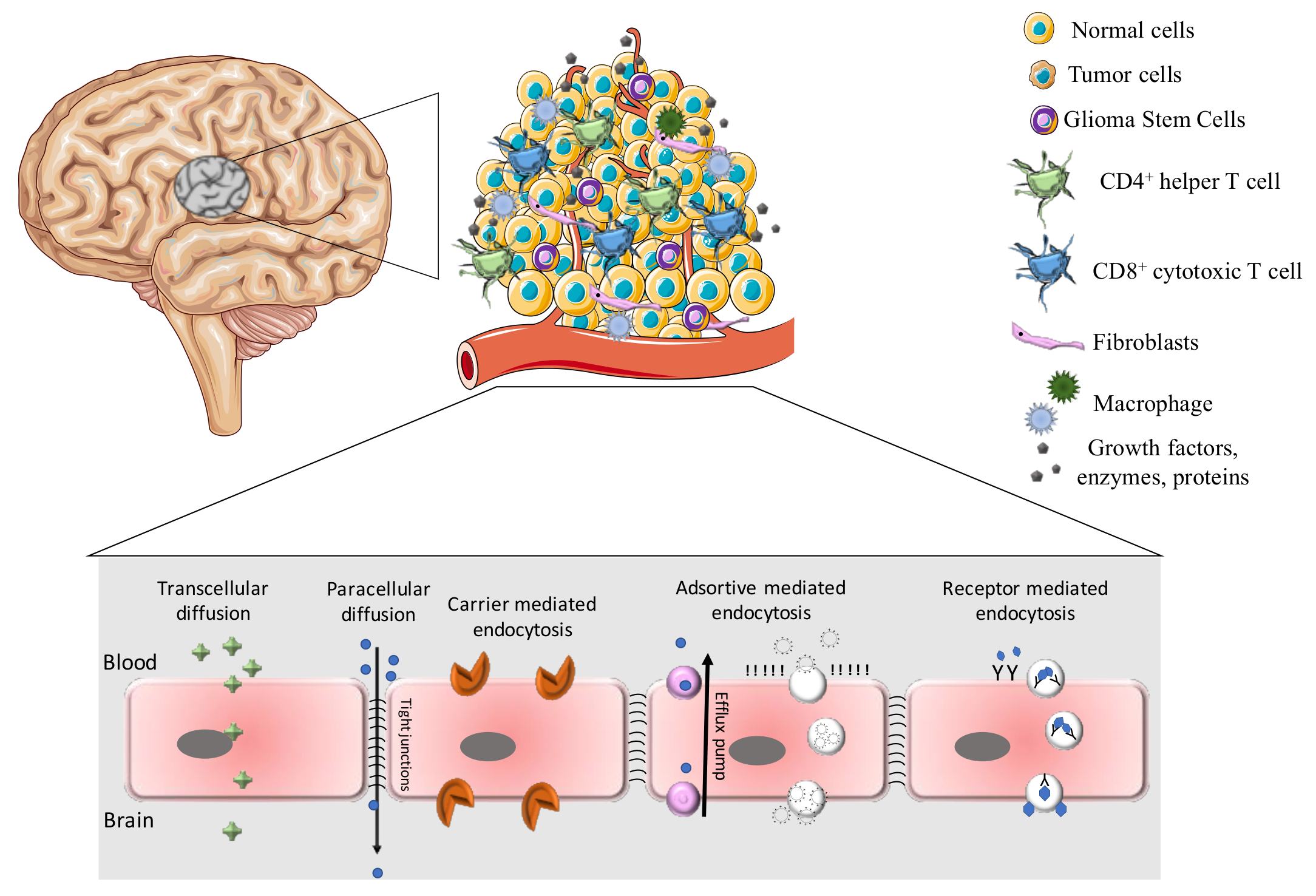
Brain tumors are a diverse group of biologically and pathologically distinct intracranial neoplasms that include tumors of neuroepithelial tissue gliomas meningeal tumors and primary lymphomas of the central nervous system non gliomas see buckner et al 2007 for review.
That being said once inside the cns the action of the immune system and the potential for antitumor response is markedly different from other sites in the body.
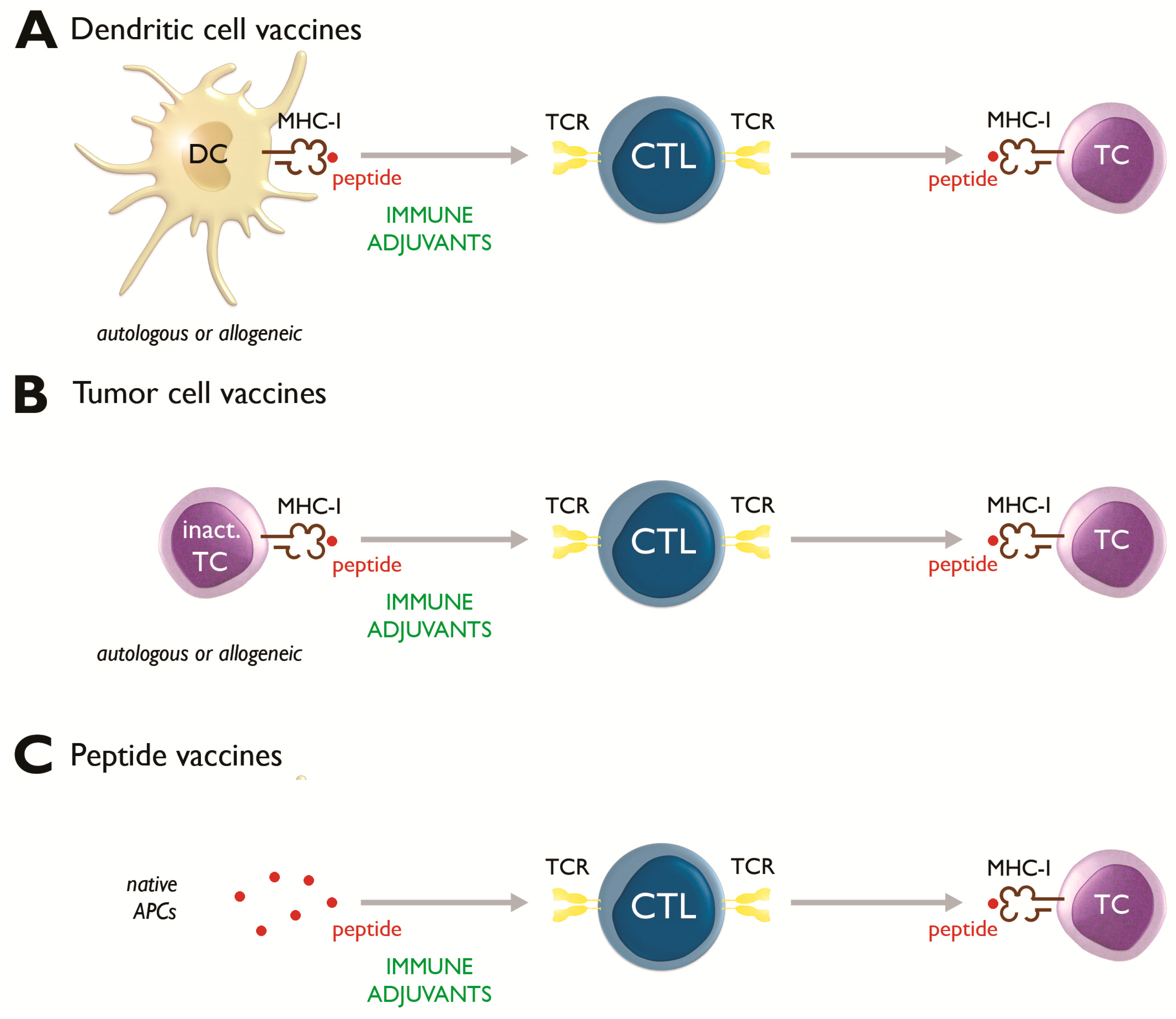
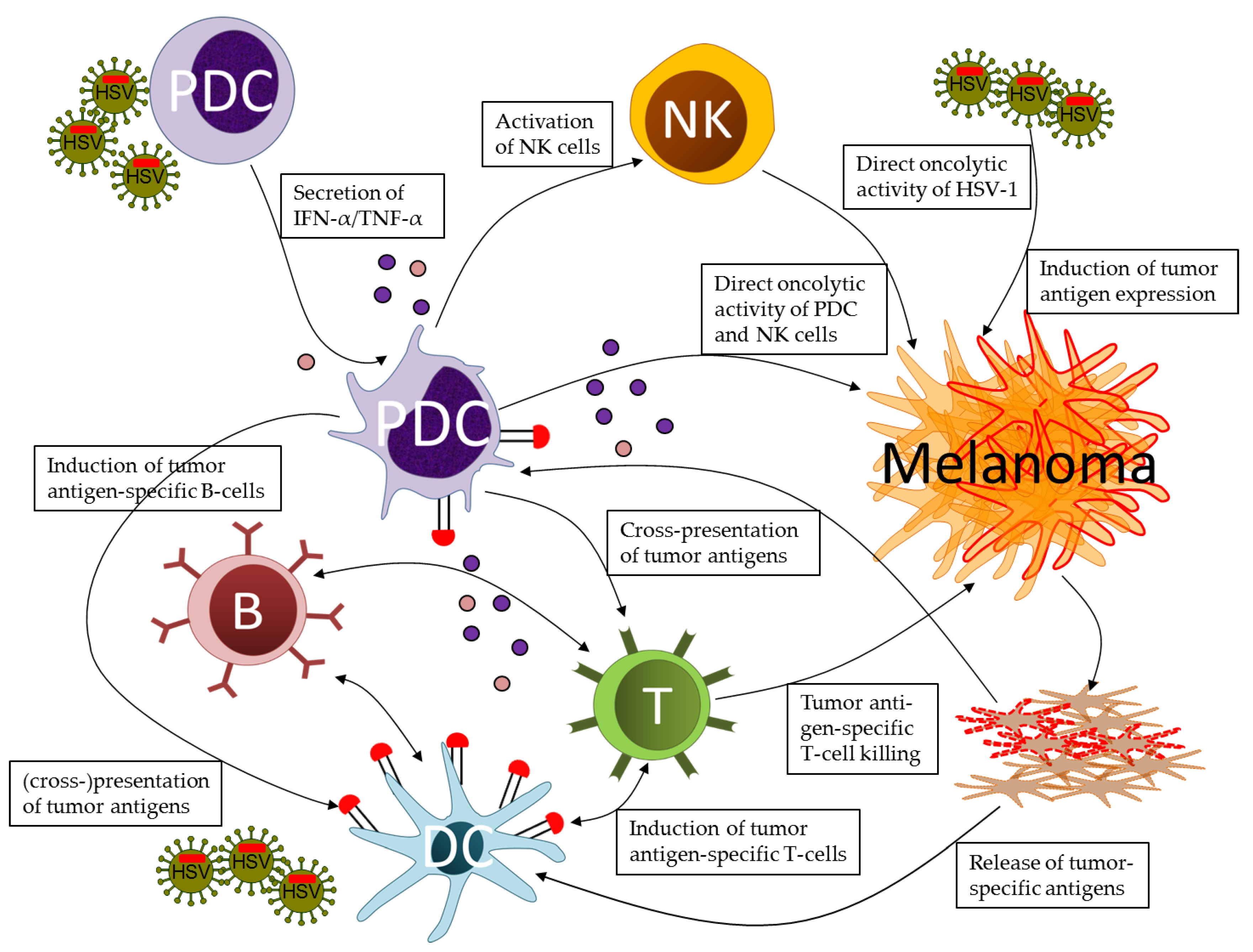
Dendritic cells guide the response of t cells to fight off invaders.
This is combined with dendritic immune cells from the person s blood.
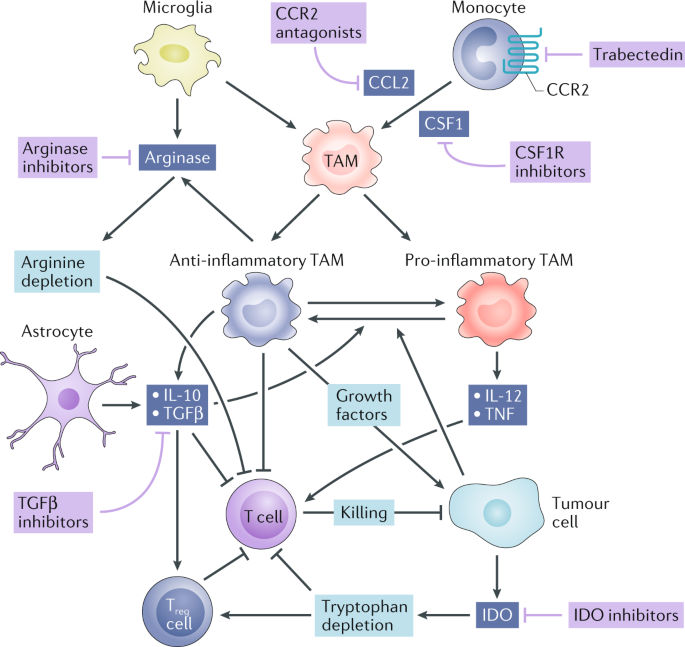
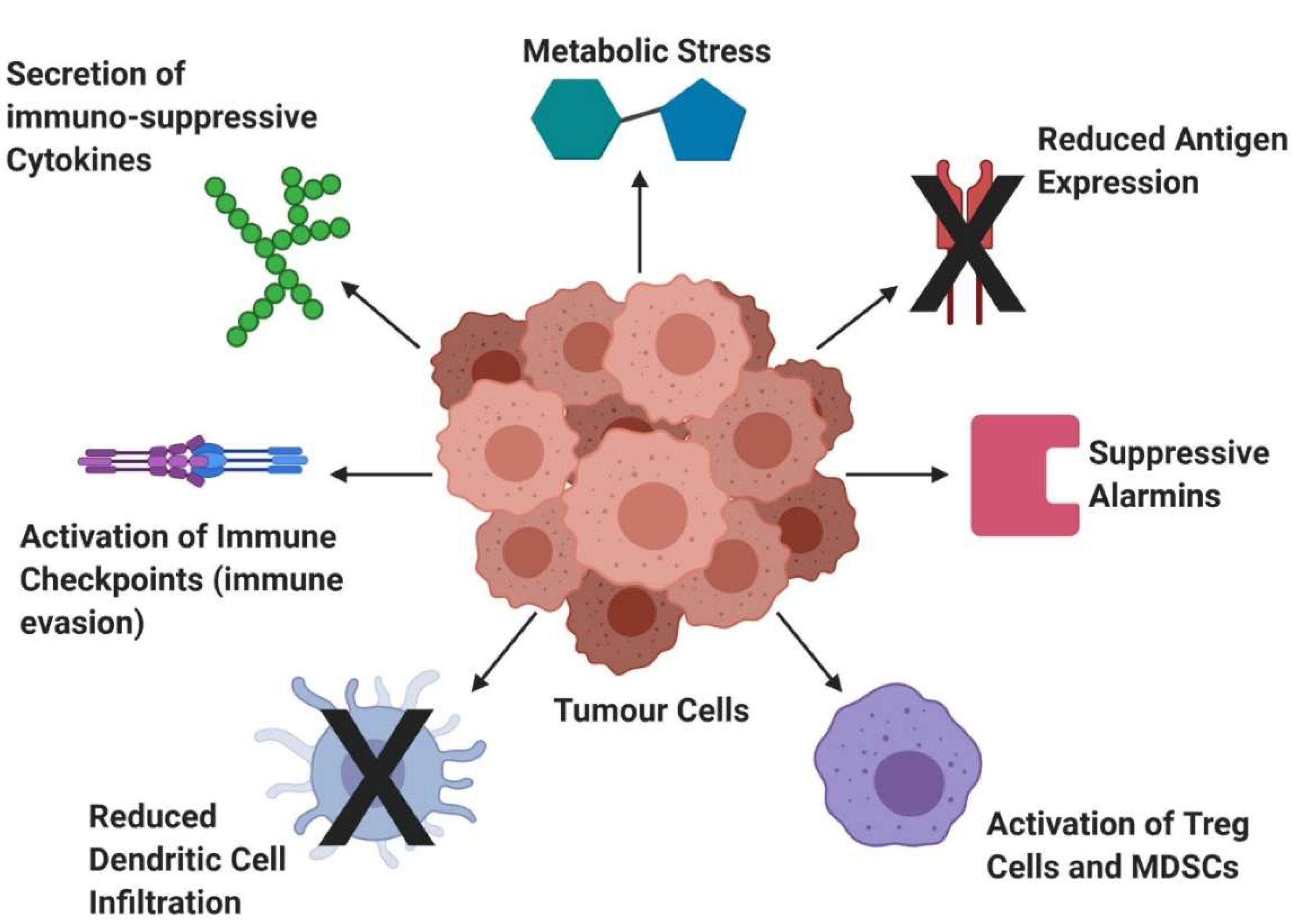
Tumor induced t cell exhaustion may be reversed through immune checkpoint blockade icb.
Of the various forms of immunotherapy dendritic cell dc based therapies are well situated to be used to induce antitumor immunity given the specialized ability of dcs to both prime and or boost innate and adaptive immune responses.
Gliomas typically arise from two different cell types in the brain astrocytes or oligodendrocytes.
Tumor cells however hijack the immune system causing t cell exhaustion and dc dysfunction.
The vaccine is called dcvax l.
This new vaccine approach focuses on dendritic cells which brody calls the generals of the immune system s army.
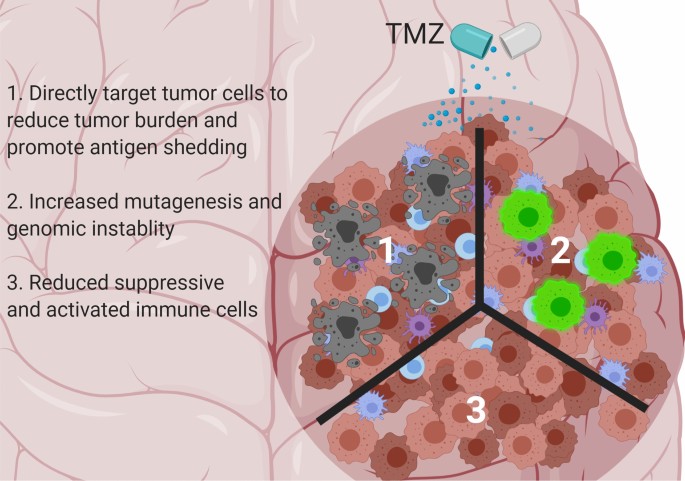
However this treatment fails to show clinical benefit in many patients.
Additionally in the presence of a tumor there can be significant blood brain barrier breakdown as well as tumor infiltrating dendritic cells macrophages and b and t lymphocytes.